《PDF制作編輯與轉換》(Corel PDF Fusion)更新v1.10/英德雙語/含注冊機[壓縮包] 簡介: 中文名 : 服務器和數據中心虛擬化 英文名 : VMware vSphere 資源格式 : 光盤鏡像 版本 : 4.0u4,4.1u2,5.0 發行時間 : 2011年08月25日 制作發行 : www.vmware.com 地區 : 美國 語言 : 簡體中文,英文 簡介 : 附近年主要版本發布時間: 5.0.0 2011/08/24 4.1 Update 2 20
電驢資源下載/磁力鏈接資源下載:
- 下載位址: [www.ed2k.online][PDF制作編輯與轉換].Corel.PDF.Fusion.v1.0.Bilingual.Incl.Keymaker-CORE.zip
- 下載位址: [www.ed2k.online][PDF制作編輯與轉換].Corel.PDF.Fusion.v1.10.Bilingual.Incl.Keymaker-CORE.zip
全選
"《PDF制作編輯與轉換》(Corel PDF Fusion)更新v1.10/英德雙語/含注冊機[壓縮包]"介紹
中文名: 服務器和數據中心虛擬化
英文名: VMware vSphere
資源格式: 光盤鏡像
版本: 4.0u4,4.1u2,5.0
發行時間: 2011年08月25日
制作發行: www.vmware.com
地區: 美國
語言: 簡體中文,英文
簡介:
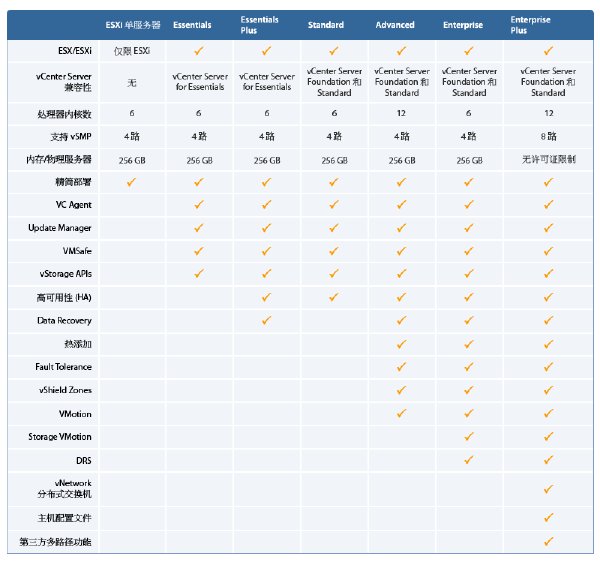
附近年主要版本發布時間:
5.0.0 2011/08/24
4.1 Update 2 2011/10/27
4.1 Update 1 2011/02/10
4.1 2010/07/13
4.0 Update 4 2011/11/17
4.0 Update 3 2011/05/05
4.0 Update 2 2010/06/10
4.0 Update 1 2009/11/19
4.0.0 2009/05/21
殺毒軟件:Norton 360
病毒庫:2011-11-21
VMware vSphere 5:最佳雲基礎架構平台
7月13日,VMware發布了 vSphere 5和雲基礎架構套件,旨在幫助客戶加快發展更為高效的自動化雲基礎架構和管理,改進管理和保護資源的方式,並最終改進IT和其服務業務之間的關系。
做為VMware最新的雲基礎架構套件的核心,VMware vSphere 5包括將近200項新增強功能,為虛擬化設定了新的標桿。VMware vSphere是全球最值得信賴、部署最廣泛的虛擬化平台。專為滿足最廣泛的虛擬和雲基礎架構需求而打造的VMware vSphere被大中小型企業、公共雲服務提供商廣泛應用,並成為日益增長的虛擬化桌面基礎設施(VDI)市場的基石。越來越多的客戶把VMware vSphere作為標准,將其作為戰略IT平台。因此,VMware vSphere吸引了廣大支持並擴展該基礎的行業領導廠商生態系統。
VMware vSphere 5 的功能和好處
VMware vSphere 5中的增強功能和新功能將為所有關鍵應用程序提供更好的應用性能以及可用性,並引入先進的自動化功能,使IT部門從手工操作中解放出來,集中精力響應業務需求,其中包括:
虛擬機規模增加 4 倍,可支持任何應用程序:憑借VMware vSphere 5,VMware將使客戶更輕松地實現100%虛擬化。VMware vSphere 5能夠運行功能比VMware vSphere 4強大4倍的虛擬機,最多支持1TB內存和32個虛擬CPU。這些虛擬機每秒能夠處理超過100萬次I/O操作。例如,VMware vSphere 5能支持每天處理超過20億次交易的數據庫。
vSphere 高可用性( HA )的更新為非計劃內停機提供了最佳保護:VMware vSphere將采用新的HA架構,它不僅能夠更輕松地設置(客戶可在幾分鐘之內通過HA設置應用程序),而且更具可擴展性,提供卓越的可用性保障。
智能策略管理:三個新的自動化增強功能將提供雲敏捷性。VMware vSphere 5將引入三個可自動化數據中心資源管理的新功能,幫助IT部門更迅速地響應業務需求,同時降低運營成本。這些功能將提供智能策略管理:對數據中心資源管理采用無需干預式方案。客戶將制定策略並建立操作參數,剩下的事情將由VMware vSphere 5來完成。VMware vSphere 5智能策略管理功能包括:
ü 自動部署將使IT部門得以隨時自動部署服務器,並能夠將部署一個含40台服務器數據中心的時間從20小時縮短至10分鐘。一旦服務器部署好並開始運行,自動部署也將對打補丁流程進行自動化,使其能夠立即將補丁應用於眾多服務器。
ü 配置驅動型存儲 將減少選擇存儲資源所需要的步驟,這是通過根據用戶定義的策略(比如:黃金級、白銀級、青銅級)來對存儲進行分組而實現的。在配置過程中,客戶輕松點擊,即可制定虛擬機所需要的服務級別,VMware vSphere將自動使用與這個服務級別相匹配的存儲資源。
ü Storage DRS 將延伸VMware於2006年首次通過 Distributed Resource Scheduler而推出的自動負載平衡功能,本次新增了存儲特性支持。一旦客戶設置了虛擬機的存儲策略,Storage DRS將自動管理存儲資源的位置和虛擬機平衡。通過對正在進行的資源分配進行自動化,Storage DRS將不再需要IT部門進行監控或干預,同時確保虛擬機保持該政策所定義的服務水平。
最小空間容納最先進的管理程序架構:VMware vSphere 5是首個完全在 ESXi上開發的VMware vSphere版本, ESXi則是唯一針對獨立於通用操作系統而運行的虛擬化而開發的管理程序。通過一個超薄架構,ESXi在不到100MB的空間裡提供業界領先的性能、可靠性和可擴展性,能夠精簡部署和配置,簡化打補丁和升級流程,並且提高了安全性。
新許可模式將 “ 池化 ” 優勢擴展至技術領域之外
在推出VMware vSphere 5的同時,VMware也改變了產品的授權模式,為客戶采用更類似雲的IT成本模式(基於用量和價值而不是物理部件和容量)奠定了基礎。VMware vSphere 5將繼續采用每處理器(CPU)許可模式,不過VMware將取消當前的CPU內核物理限制和每服務器物理RAM限制,代之以基於虛擬化內存池(或稱為vRAM)的軟件授權模式 。
vRAM池是指客戶環境下所有虛擬機配備的內存總數量。每持有一份vSphere 5 CPU許可,購買者可獲得特定數量的vRAM,這些vRAM可以在整個vSphere環境下池化,實現真正的基於雲或效用計算的IT消費模式。vRAM容量在虛擬機之間的分配不受限制:客戶可以配置多個小型虛擬機,也可配置成一個大型虛擬機。VMware vSphere將CPU、內存、存儲和網絡集結成池,幫助客戶實現硬件利用率和效率的最大化。利用這些許可變化,VMware將“池化”的概念由技術領域擴展到業務領域(“池化”正是雲計算的基本組件之一),建立基於池化的許可授權,實現利用率和價值的最大化。
VMware vSphere 5仍采用每CPU的許可模式,因此客戶可以繼續利用已經建立起來的購買、部署和許可管理流程。欲了解有關VMware vSphere 5授權的更多信息,請訪問: http://www.vmware.com/files/pdf/vsphere_pricing.pdf
_________________________________________________________________________
|×××××××××××××××××××以下為vSphere v4.x的介紹×××××××××××××××××××|
|________________________________________________________________________|
What’s New in vSphere 4.1
With this release, the VMware virtual datacenter operating system continues to transform x86 IT infrastructure into the most efficient, shared, on-demand utility, with built-in availability, scalability, and security services for all applications and simple, proactive automated management. The new and enhanced features in vSphere 4.1 are listed below.
* Installation and Deployment
* Storage
* Network
* Availability
* Management
* Platform Enhancements
* Partner Ecosystem
Installation and Deployment
* VMware ESX. VMware vSphere 4.1 and its subsequent update and patch releases are the last releases to include both ESX and ESXi hypervisor architectures. Future major releases of VMware vSphere will include only the VMware ESXi architecture.
o VMware recommends that customers start transitioning to the ESXi architecture when deploying VMware vSphere 4.1.
o VMware will continue to provide technical support for VMware ESX according to the VMware vSphere support policy.
o To learn more about the ESXi architecture and how to migrate from ESX to ESXi, go to the VMware ESX to ESXi Upgrade Center.
* Scripted Install for ESXi. Scripted installation of ESXi to local and remote disks allows rapid deployment of ESXi to many machines. You can start the scripted installation with a CD-ROM drive or over the network by using PXE booting. You cannot use scripted installation to install ESXi to a USB device. See the ESX and vCenter Server Installation Guide, the ESXi Installable and vCenter Server Setup Guide, and the ESXi Embedded and vCenter Server Setup Guide.
* vSphere Client Removal from ESX/ESXi Builds. For ESX and ESXi, the vSphere Client is available for download from the VMware Web site. It is no longer packaged with builds of ESX and ESXi. After installing ESX and ESXi, users are directed to the download page on the VMware Web site to get the compatible vSphere Client for that release. The vSphere Client is still packaged with builds of vCenter Server. See the ESX and vCenter Server Installation Guide, the ESXi Installable and vCenter Server Setup Guide, and the ESXi Embedded and vCenter Server Setup Guide.
Storage
* Boot from SAN. vSphere 4.1 enables ESXi boot from SAN (BFN). iSCSI, FCoE, and Fibre Channel boot are supported. Refer to the Hardware Compatibility Guide for the latest list of NICs and Converged Adapters that are supported with iSCSI boot. See the iSCSI SAN Configuration Guide and the Fibre Channel SAN Configuration Guide.
* Hardware Acceleration with vStorage APIs for Array Integration (VAAI). ESX can offload specific storage operations to compliant storage hardware. With storage hardware assistance, ESX performs these operations faster and consumes less CPU, memory, and storage fabric bandwidth. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* Storage Performance Statistics. vSphere 4.1 offers enhanced visibility into storage throughput and latency of hosts and virtual machines, and aids in troubleshooting storage performance issues. NFS statistics are now available in vCenter Server performance charts, as well as esxtop. New VMDK and datastore statistics are included. All statistics are available through the vSphere SDK. See the vSphere Datacenter Administration Guide.
* Storage I/O Control. This feature provides quality-of-service capabilities for storage I/O in the form of I/O shares and limits that are enforced across all virtual machines accessing a datastore, regardless of which host they are running on. Using Storage I/O Control, vSphere administrators can ensure that the most important virtual machines get adequate I/O resources even in times of congestion. See the vSphere Resource Management Guide.
* iSCSI Hardware Offloads. vSphere 4.1 enables 10Gb iSCSI hardware offloads (Broadcom 57711) and 1Gb iSCSI hardware offloads (Broadcom 5709). See the ESX Configuration Guide, the ESXi Configuration Guide, and the iSCSI SAN Configuration Guide.
* NFS Performance Enhancements. Networking performance for NFS has been optimized to improve throughput and reduce CPU usage. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
Network
* Network I/O Control. Traffic-management controls allow flexible partitioning of physical NIC bandwidth between different traffic types, including virtual machine, vMotion, FT, and IP storage traffic (vNetwork Distributed Switch only). See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* IPv6 Enhancements. IPv6 in ESX supports Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) with manual keying. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* Load-Based Teaming. vSphere 4.1 allows dynamic adjustment of the teaming algorithm so that the load is always balanced across a team of physical adapters on a vNetwork Distributed Switch. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* E1000 vNIC Enhancements. E1000 vNIC supports jumbo frames in vSphere 4.1. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
Availability
* Windows Failover Clustering with VMware HA. Clustered Virtual Machines that utilize Windows Failover Clustering/Microsoft Cluster Service are now fully supported in conjunction with VMware HA. See Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service.
* VMware HA Scalability Improvements. VMware HA has the same limits for virtual machines per host, hosts per cluster, and virtual machines per cluster as vSphere. See Configuration Maximums for VMware vSphere 4.1 for details about the limitations for this release.
* VMware HA Healthcheck and Operational Status. The VMware HA dashboard in the vSphere Client provides a new detailed window called Cluster Operational Status. This window displays more information about the current VMware HA operational status, including the specific status and errors for each host in the VMware HA cluster. See the vSphere Availability Guide.
* VMware Fault Tolerance (FT) Enhancements. vSphere 4.1 introduces an FT-specific versioning-control mechanism that allows the Primary and Secondary VMs to run on FT-compatible hosts at different but compatible patch levels. vSphere 4.1 differentiates between events that are logged for a Primary VM and those that are logged for its Secondary VM, and reports why a host might not support FT. In addition, you can disable VMware HA when FT-enabled virtual machines are deployed in a cluster, allowing for cluster maintenance operations without turning off FT. See the vSphere Availability Guide.
* DRS Interoperability for VMware HA and Fault Tolerance (FT). FT-enabled virtual machines can take advantage of DRS functionality for load balancing and initial placement. In addition, VMware HA and DRS are tightly integrated, which allows VMware HA to restart virtual machines in more situations. See the vSphere Availability Guide.
* Enhanced Network Logging Performance. Fault Tolerance (FT) network logging performance allows improved throughput and reduced CPU usage. In addition, you can use vmxnet3 vNICs in FT-enabled virtual machines. See the vSphere Availability Guide.
* Concurrent VMware Data Recovery Sessions. vSphere 4.1 provides the ability to concurrently manage multiple VMware Data Recovery appliances. See the VMware Data Recovery Administration Guide.
* vStorage APIs for Data Protection (VADP) Enhancements. VADP now offers VSS quiescing support for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 servers. This enables application-consistent backup and restore operations for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 applications.
Management
* vCLI Enhancements. vCLI adds options for SCSI, VAAI, network, and virtual machine control, including the ability to terminate an unresponsive virtual machine. In addition, vSphere 4.1 provides controls that allow you to log vCLI activity. See the vSphere Command-Line Interface Installation and Scripting Guide and the vSphere Command-Line Interface Reference.
* Lockdown Mode Enhancements. VMware ESXi 4.1 lockdown mode allows the administrator to tightly restrict access to the ESXi Direct Console User Interface (DCUI) and Tech Support Mode (TSM). When lockdown mode is enabled, DCUI access is restricted to the root user, while access to Tech Support Mode is completely disabled for all users. With lockdown mode enabled, access to the host for management or monitoring using CIM is possible only through vCenter Server. Direct access to the host using the vSphere Client is not permitted. See the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* Access Virtual Machine Serial Ports Over the Network. You can redirect virtual machine serial ports over a standard network link in vSphere 4.1. This enables solutions such as third-party virtual serial port concentrators for virtual machine serial console management or monitoring. See the vSphere Virtual Machine Administration Guide.
* vCenter Converter Hyper-V Import. vCenter Converter allows users to point to a Hyper-V machine. Converter displays the virtual machines running on the Hyper-V system, and users can select a powered-off virtual machine to import to a VMware destination. See the vCenter Converter Installation and Administration Guide.
* Enhancements to Host Profiles. You can use Host Profiles to roll out administrator password changes in vSphere 4.1. Enhancements also include improved Cisco Nexus 1000V support and PCI device ordering configuration. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* Unattended Authentication in vSphere Management Assistant (vMA). vMA 4.1 offers improved authentication capability, including integration with Active Directory and commands to configure the connection. See VMware vSphere Management Assistant.
* Updated Deployment Environment in vSphere Management Assistant (vMA). The updated deployment environment in vMA 4.1 is fully compatible with vMA 4.0. A significant change is the transition from RHEL to CentOS. See VMware vSphere Management Assistant.
* vCenter Orchestrator 64-bit Support. vCenter Orchestrator 4.1 provides a client and server for 64-bit installations, with an optional 32-bit client. The performance of the Orchestrator server on 64-bit installations is greatly enhanced, as compared to running the server on a 32-bit machine. See the vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide.
* Improved Support for Handling Recalled Patches in vCenter Update Manager. Update Manager 4.1 immediately sends critical notifications about recalled ESX and related patches. In addition, Update Manager prevents you from installing a recalled patch that you might have already downloaded. This feature also helps you identify hosts where recalled patches might already be installed. See the vCenter Update Manager Installation and Administration Guide.
* License Reporting Manager. The License Reporting Manager provides a centralized interface for all license keys for vSphere 4.1 products in a virtual IT infrastructure and their respective usage. You can view and generate reports on license keys and usage for different time periods with the License Reporting Manager. A historical record of the utilization per license key is maintained in the vCenter Server database. See the vSphere Datacenter Administration Guide.
* Power Management Improvements. ESX 4.1 takes advantage of deep sleep states to further reduce power consumption during idle periods. The vSphere Client has a simple user interface that allows you to choose one of four host power management policies. In addition, you can view the history of host power consumption and power cap information on the vSphere Client Performance tab on newer platforms with integrated power meters. See the vSphere Datacenter Administration Guide.
Platform Enhancements
* Performance and Scalability Improvements. vSphere 4.1 includes numerous enhancements that increase performance and scalability.
o vCenter Server 4.1 can support three times more virtual machines and hosts per system, as well as more concurrent instances of the vSphere Client and a larger number of virtual machines per cluster than vCenter Server 4.0. The scalability limits of Linked Mode, vMotion, and vNetwork Distributed Switch have also increased.
o New optimizations have been implemented for AMD-V and Intel VT-x architectures, while memory utilization efficiency has been improved still further using Memory Compression. Storage enhancements have led to significant performance improvements in NFS environments. VDI operations, virtual machine provisioning and power operations, and vMotion have enhanced performance as well.
See Configuration Maximums for VMware vSphere 4.1.
* Reduced Overhead Memory. vSphere 4.1 reduces the amount of overhead memory required, especially when running large virtual machines on systems with CPUs that provide hardware MMU support (AMD RVI or Intel EPT).
* DRS Virtual Machine Host Affinity Rules. DRS provides the ability to set constraints that restrict placement of a virtual machine to a subset of hosts in a cluster. This feature is useful for enforcing host-based ISV licensing models, as well as keeping sets of virtual machines on different racks or blade systems for availability reasons. See the vSphere Resource Management Guide.
* Memory Compression. Compressed memory is a new level of the memory hierarchy, between RAM and disk. Slower than memory, but much faster than disk, compressed memory improves the performance of virtual machines when memory is under contention, because less virtual memory is swapped to disk. See the vSphere Resource Management Guide.
* vMotion Enhancements. In vSphere 4.1, vMotion enhancements significantly reduce the overall time for host evacuations, with support for more simultaneous virtual machine migrations and faster individual virtual machine migrations. The result is a performance improvement of up to 8x for an individual virtual machine migration, and support for four to eight simultaneous vMotion migrations per host, depending on the vMotion network adapter (1GbE or 10GbE respectively). See the vSphere Datacenter Administration Guide.
* ESX/ESXi Active Directory Integration. Integration with Microsoft Active Directory allows seamless user authentication for ESX/ESXi. You can maintain users and groups in Active Directory for centralized user management and you can assign privileges to users or groups on ESX/ESXi hosts. In vSphere 4.1, integration with Active Directory allows you to roll out permission rules to hosts by using Host Profiles. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* Configuring USB Device Passthrough from an ESX/ESXi Host to a Virtual Machine. You can configure a virtual machine to use USB devices that are connected to an ESX/ESXi host where the virtual machine is running. The connection is maintained even if you migrate the virtual machine using vMotion. See the vSphere Virtual Machine Administration Guide.
* Improvements in Enhanced vMotion Compatibility. vSphere 4.1 includes an AMD Opteron Gen. 3 (no 3DNow!™) EVC mode that prepares clusters for vMotion compatibility with future AMD processors. EVC also provides numerous usability improvements, including the display of EVC modes for virtual machines, more timely error detection, better error messages, and the reduced need to restart virtual machines. See the vSphere Datacenter Administration Guide.
Partner Ecosystem
* vCenter Update Manager Support for Provisioning, Patching, and Upgrading EMC's ESX PowerPath Module. vCenter Update Manager can provision, patch, and upgrade third-party modules that you can install on ESX, such as EMC's PowerPath multipathing software. Using the capability of Update Manager to set policies using the Baseline construct and the comprehensive Compliance Dashboard, you can simplify provisioning, patching, and upgrade of the PowerPath module at scale. See the vCenter Update Manager Installation and Administration Guide.
* User-configurable Number of Virtual CPUs per Virtual Socket. You can configure virtual machines to have multiple virtual CPUs reside in a single virtual socket, with each virtual CPU appearing to the guest operating system as a single core. Previously, virtual machines were restricted to having only one virtual CPU per virtual socket. See the vSphere Virtual Machine Administration Guide.
* Expanded List of Supported Processors. The list of supported processors has been expanded for ESX 4.1. To determine which processors are compatible with this release, use the Hardware Compatibility Guide. Among the supported processors is the Intel Xeon 7500 Series processor, code-named Nehalem-EX (up to 8 sockets).
_________________________________________________________________
2010年7月17日,重新上傳vCenter源;附加esx4.0-4.1、esxi4.0-4.1升級包。
_________________________________________________________________
2010年7月23日,增加Dell定制的ESXi4.1;原文件名:VMware-VMvisor-InstallerCD-4.1-260247.i386_DellCustomized_A00.iso
_________________________________________________________________
2010年8月02日,增加ESXi3.5-ESXi4.1升級包;原文件名:upgrade-from-ESXi3.5-to-4.1.0-0.0.260247-release.zip
_________________________________________________________________
2010年08月19日,增加"pre-upgrade-from-ESX4.0-to-4.1.0-0.0.260247-release.zip"
_________________________________________________________________
2010年09月11日,增加"VMware-vShield-Manager-4.1.0-287872.ova"
注:ova是一種預先設置好了的虛擬機“模板”,導入後就可以使用。
_________________________________________________________________
2011年03月06日,增加"VMware vShield 4.1u1"相關資源
_________________________________________________________________
2011年03月26日,增加“VMwareDataRecovery 1.2.1”相關資源
_________________________________________________________________
2011年04月14日,增加“VMware Workstation 2011”相關資源
_________________________________________________________________
2011年06月01日,增加"vSphere 4.0u3"部分資源
_________________________________________________________________
2011年06月29日,增加"vCenter Converter Standalone 5.0 Beta"資源
_________________________________________________________________
2011年08月26日,增加"vSphere 5.0"資源(逐步上傳,無VSA資源)
_________________________________________________________________
2011年09月03日,增加vSphere 5.0相關說明以及“vCenter Converter Standalone 5.0”正式版資源(beta版的資源即將刪除)
_________________________________________________________________
2011年11月06-08日,完善及增加"vSphere 4.0u3"和"vSphere 4.1u2"資源。
_________________________________________________________________
2011年12月22日,增加了"ESXi4.1"和"ESXi5.0"的補丁包資源。
_________________________________________________________________
英文名: VMware vSphere
資源格式: 光盤鏡像
版本: 4.0u4,4.1u2,5.0
發行時間: 2011年08月25日
制作發行: www.vmware.com
地區: 美國
語言: 簡體中文,英文
簡介:

附近年主要版本發布時間:
5.0.0 2011/08/24
4.1 Update 2 2011/10/27
4.1 Update 1 2011/02/10
4.1 2010/07/13
4.0 Update 4 2011/11/17
4.0 Update 3 2011/05/05
4.0 Update 2 2010/06/10
4.0 Update 1 2009/11/19
4.0.0 2009/05/21
殺毒軟件:Norton 360
病毒庫:2011-11-21
VMware vSphere 5:最佳雲基礎架構平台
7月13日,VMware發布了 vSphere 5和雲基礎架構套件,旨在幫助客戶加快發展更為高效的自動化雲基礎架構和管理,改進管理和保護資源的方式,並最終改進IT和其服務業務之間的關系。
做為VMware最新的雲基礎架構套件的核心,VMware vSphere 5包括將近200項新增強功能,為虛擬化設定了新的標桿。VMware vSphere是全球最值得信賴、部署最廣泛的虛擬化平台。專為滿足最廣泛的虛擬和雲基礎架構需求而打造的VMware vSphere被大中小型企業、公共雲服務提供商廣泛應用,並成為日益增長的虛擬化桌面基礎設施(VDI)市場的基石。越來越多的客戶把VMware vSphere作為標准,將其作為戰略IT平台。因此,VMware vSphere吸引了廣大支持並擴展該基礎的行業領導廠商生態系統。
VMware vSphere 5 的功能和好處
VMware vSphere 5中的增強功能和新功能將為所有關鍵應用程序提供更好的應用性能以及可用性,並引入先進的自動化功能,使IT部門從手工操作中解放出來,集中精力響應業務需求,其中包括:
虛擬機規模增加 4 倍,可支持任何應用程序:憑借VMware vSphere 5,VMware將使客戶更輕松地實現100%虛擬化。VMware vSphere 5能夠運行功能比VMware vSphere 4強大4倍的虛擬機,最多支持1TB內存和32個虛擬CPU。這些虛擬機每秒能夠處理超過100萬次I/O操作。例如,VMware vSphere 5能支持每天處理超過20億次交易的數據庫。
vSphere 高可用性( HA )的更新為非計劃內停機提供了最佳保護:VMware vSphere將采用新的HA架構,它不僅能夠更輕松地設置(客戶可在幾分鐘之內通過HA設置應用程序),而且更具可擴展性,提供卓越的可用性保障。
智能策略管理:三個新的自動化增強功能將提供雲敏捷性。VMware vSphere 5將引入三個可自動化數據中心資源管理的新功能,幫助IT部門更迅速地響應業務需求,同時降低運營成本。這些功能將提供智能策略管理:對數據中心資源管理采用無需干預式方案。客戶將制定策略並建立操作參數,剩下的事情將由VMware vSphere 5來完成。VMware vSphere 5智能策略管理功能包括:
ü 自動部署將使IT部門得以隨時自動部署服務器,並能夠將部署一個含40台服務器數據中心的時間從20小時縮短至10分鐘。一旦服務器部署好並開始運行,自動部署也將對打補丁流程進行自動化,使其能夠立即將補丁應用於眾多服務器。
ü 配置驅動型存儲 將減少選擇存儲資源所需要的步驟,這是通過根據用戶定義的策略(比如:黃金級、白銀級、青銅級)來對存儲進行分組而實現的。在配置過程中,客戶輕松點擊,即可制定虛擬機所需要的服務級別,VMware vSphere將自動使用與這個服務級別相匹配的存儲資源。
ü Storage DRS 將延伸VMware於2006年首次通過 Distributed Resource Scheduler而推出的自動負載平衡功能,本次新增了存儲特性支持。一旦客戶設置了虛擬機的存儲策略,Storage DRS將自動管理存儲資源的位置和虛擬機平衡。通過對正在進行的資源分配進行自動化,Storage DRS將不再需要IT部門進行監控或干預,同時確保虛擬機保持該政策所定義的服務水平。
最小空間容納最先進的管理程序架構:VMware vSphere 5是首個完全在 ESXi上開發的VMware vSphere版本, ESXi則是唯一針對獨立於通用操作系統而運行的虛擬化而開發的管理程序。通過一個超薄架構,ESXi在不到100MB的空間裡提供業界領先的性能、可靠性和可擴展性,能夠精簡部署和配置,簡化打補丁和升級流程,並且提高了安全性。
新許可模式將 “ 池化 ” 優勢擴展至技術領域之外
在推出VMware vSphere 5的同時,VMware也改變了產品的授權模式,為客戶采用更類似雲的IT成本模式(基於用量和價值而不是物理部件和容量)奠定了基礎。VMware vSphere 5將繼續采用每處理器(CPU)許可模式,不過VMware將取消當前的CPU內核物理限制和每服務器物理RAM限制,代之以基於虛擬化內存池(或稱為vRAM)的軟件授權模式 。
vRAM池是指客戶環境下所有虛擬機配備的內存總數量。每持有一份vSphere 5 CPU許可,購買者可獲得特定數量的vRAM,這些vRAM可以在整個vSphere環境下池化,實現真正的基於雲或效用計算的IT消費模式。vRAM容量在虛擬機之間的分配不受限制:客戶可以配置多個小型虛擬機,也可配置成一個大型虛擬機。VMware vSphere將CPU、內存、存儲和網絡集結成池,幫助客戶實現硬件利用率和效率的最大化。利用這些許可變化,VMware將“池化”的概念由技術領域擴展到業務領域(“池化”正是雲計算的基本組件之一),建立基於池化的許可授權,實現利用率和價值的最大化。
VMware vSphere 5仍采用每CPU的許可模式,因此客戶可以繼續利用已經建立起來的購買、部署和許可管理流程。欲了解有關VMware vSphere 5授權的更多信息,請訪問: http://www.vmware.com/files/pdf/vsphere_pricing.pdf
_________________________________________________________________________
|×××××××××××××××××××以下為vSphere v4.x的介紹×××××××××××××××××××|
|________________________________________________________________________|
What’s New in vSphere 4.1
With this release, the VMware virtual datacenter operating system continues to transform x86 IT infrastructure into the most efficient, shared, on-demand utility, with built-in availability, scalability, and security services for all applications and simple, proactive automated management. The new and enhanced features in vSphere 4.1 are listed below.
* Installation and Deployment
* Storage
* Network
* Availability
* Management
* Platform Enhancements
* Partner Ecosystem
Installation and Deployment
* VMware ESX. VMware vSphere 4.1 and its subsequent update and patch releases are the last releases to include both ESX and ESXi hypervisor architectures. Future major releases of VMware vSphere will include only the VMware ESXi architecture.
o VMware recommends that customers start transitioning to the ESXi architecture when deploying VMware vSphere 4.1.
o VMware will continue to provide technical support for VMware ESX according to the VMware vSphere support policy.
o To learn more about the ESXi architecture and how to migrate from ESX to ESXi, go to the VMware ESX to ESXi Upgrade Center.
* Scripted Install for ESXi. Scripted installation of ESXi to local and remote disks allows rapid deployment of ESXi to many machines. You can start the scripted installation with a CD-ROM drive or over the network by using PXE booting. You cannot use scripted installation to install ESXi to a USB device. See the ESX and vCenter Server Installation Guide, the ESXi Installable and vCenter Server Setup Guide, and the ESXi Embedded and vCenter Server Setup Guide.
* vSphere Client Removal from ESX/ESXi Builds. For ESX and ESXi, the vSphere Client is available for download from the VMware Web site. It is no longer packaged with builds of ESX and ESXi. After installing ESX and ESXi, users are directed to the download page on the VMware Web site to get the compatible vSphere Client for that release. The vSphere Client is still packaged with builds of vCenter Server. See the ESX and vCenter Server Installation Guide, the ESXi Installable and vCenter Server Setup Guide, and the ESXi Embedded and vCenter Server Setup Guide.
Storage
* Boot from SAN. vSphere 4.1 enables ESXi boot from SAN (BFN). iSCSI, FCoE, and Fibre Channel boot are supported. Refer to the Hardware Compatibility Guide for the latest list of NICs and Converged Adapters that are supported with iSCSI boot. See the iSCSI SAN Configuration Guide and the Fibre Channel SAN Configuration Guide.
* Hardware Acceleration with vStorage APIs for Array Integration (VAAI). ESX can offload specific storage operations to compliant storage hardware. With storage hardware assistance, ESX performs these operations faster and consumes less CPU, memory, and storage fabric bandwidth. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* Storage Performance Statistics. vSphere 4.1 offers enhanced visibility into storage throughput and latency of hosts and virtual machines, and aids in troubleshooting storage performance issues. NFS statistics are now available in vCenter Server performance charts, as well as esxtop. New VMDK and datastore statistics are included. All statistics are available through the vSphere SDK. See the vSphere Datacenter Administration Guide.
* Storage I/O Control. This feature provides quality-of-service capabilities for storage I/O in the form of I/O shares and limits that are enforced across all virtual machines accessing a datastore, regardless of which host they are running on. Using Storage I/O Control, vSphere administrators can ensure that the most important virtual machines get adequate I/O resources even in times of congestion. See the vSphere Resource Management Guide.
* iSCSI Hardware Offloads. vSphere 4.1 enables 10Gb iSCSI hardware offloads (Broadcom 57711) and 1Gb iSCSI hardware offloads (Broadcom 5709). See the ESX Configuration Guide, the ESXi Configuration Guide, and the iSCSI SAN Configuration Guide.
* NFS Performance Enhancements. Networking performance for NFS has been optimized to improve throughput and reduce CPU usage. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
Network
* Network I/O Control. Traffic-management controls allow flexible partitioning of physical NIC bandwidth between different traffic types, including virtual machine, vMotion, FT, and IP storage traffic (vNetwork Distributed Switch only). See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* IPv6 Enhancements. IPv6 in ESX supports Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) with manual keying. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* Load-Based Teaming. vSphere 4.1 allows dynamic adjustment of the teaming algorithm so that the load is always balanced across a team of physical adapters on a vNetwork Distributed Switch. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* E1000 vNIC Enhancements. E1000 vNIC supports jumbo frames in vSphere 4.1. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
Availability
* Windows Failover Clustering with VMware HA. Clustered Virtual Machines that utilize Windows Failover Clustering/Microsoft Cluster Service are now fully supported in conjunction with VMware HA. See Setup for Failover Clustering and Microsoft Cluster Service.
* VMware HA Scalability Improvements. VMware HA has the same limits for virtual machines per host, hosts per cluster, and virtual machines per cluster as vSphere. See Configuration Maximums for VMware vSphere 4.1 for details about the limitations for this release.
* VMware HA Healthcheck and Operational Status. The VMware HA dashboard in the vSphere Client provides a new detailed window called Cluster Operational Status. This window displays more information about the current VMware HA operational status, including the specific status and errors for each host in the VMware HA cluster. See the vSphere Availability Guide.
* VMware Fault Tolerance (FT) Enhancements. vSphere 4.1 introduces an FT-specific versioning-control mechanism that allows the Primary and Secondary VMs to run on FT-compatible hosts at different but compatible patch levels. vSphere 4.1 differentiates between events that are logged for a Primary VM and those that are logged for its Secondary VM, and reports why a host might not support FT. In addition, you can disable VMware HA when FT-enabled virtual machines are deployed in a cluster, allowing for cluster maintenance operations without turning off FT. See the vSphere Availability Guide.
* DRS Interoperability for VMware HA and Fault Tolerance (FT). FT-enabled virtual machines can take advantage of DRS functionality for load balancing and initial placement. In addition, VMware HA and DRS are tightly integrated, which allows VMware HA to restart virtual machines in more situations. See the vSphere Availability Guide.
* Enhanced Network Logging Performance. Fault Tolerance (FT) network logging performance allows improved throughput and reduced CPU usage. In addition, you can use vmxnet3 vNICs in FT-enabled virtual machines. See the vSphere Availability Guide.
* Concurrent VMware Data Recovery Sessions. vSphere 4.1 provides the ability to concurrently manage multiple VMware Data Recovery appliances. See the VMware Data Recovery Administration Guide.
* vStorage APIs for Data Protection (VADP) Enhancements. VADP now offers VSS quiescing support for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 servers. This enables application-consistent backup and restore operations for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 applications.
Management
* vCLI Enhancements. vCLI adds options for SCSI, VAAI, network, and virtual machine control, including the ability to terminate an unresponsive virtual machine. In addition, vSphere 4.1 provides controls that allow you to log vCLI activity. See the vSphere Command-Line Interface Installation and Scripting Guide and the vSphere Command-Line Interface Reference.
* Lockdown Mode Enhancements. VMware ESXi 4.1 lockdown mode allows the administrator to tightly restrict access to the ESXi Direct Console User Interface (DCUI) and Tech Support Mode (TSM). When lockdown mode is enabled, DCUI access is restricted to the root user, while access to Tech Support Mode is completely disabled for all users. With lockdown mode enabled, access to the host for management or monitoring using CIM is possible only through vCenter Server. Direct access to the host using the vSphere Client is not permitted. See the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* Access Virtual Machine Serial Ports Over the Network. You can redirect virtual machine serial ports over a standard network link in vSphere 4.1. This enables solutions such as third-party virtual serial port concentrators for virtual machine serial console management or monitoring. See the vSphere Virtual Machine Administration Guide.
* vCenter Converter Hyper-V Import. vCenter Converter allows users to point to a Hyper-V machine. Converter displays the virtual machines running on the Hyper-V system, and users can select a powered-off virtual machine to import to a VMware destination. See the vCenter Converter Installation and Administration Guide.
* Enhancements to Host Profiles. You can use Host Profiles to roll out administrator password changes in vSphere 4.1. Enhancements also include improved Cisco Nexus 1000V support and PCI device ordering configuration. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* Unattended Authentication in vSphere Management Assistant (vMA). vMA 4.1 offers improved authentication capability, including integration with Active Directory and commands to configure the connection. See VMware vSphere Management Assistant.
* Updated Deployment Environment in vSphere Management Assistant (vMA). The updated deployment environment in vMA 4.1 is fully compatible with vMA 4.0. A significant change is the transition from RHEL to CentOS. See VMware vSphere Management Assistant.
* vCenter Orchestrator 64-bit Support. vCenter Orchestrator 4.1 provides a client and server for 64-bit installations, with an optional 32-bit client. The performance of the Orchestrator server on 64-bit installations is greatly enhanced, as compared to running the server on a 32-bit machine. See the vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide.
* Improved Support for Handling Recalled Patches in vCenter Update Manager. Update Manager 4.1 immediately sends critical notifications about recalled ESX and related patches. In addition, Update Manager prevents you from installing a recalled patch that you might have already downloaded. This feature also helps you identify hosts where recalled patches might already be installed. See the vCenter Update Manager Installation and Administration Guide.
* License Reporting Manager. The License Reporting Manager provides a centralized interface for all license keys for vSphere 4.1 products in a virtual IT infrastructure and their respective usage. You can view and generate reports on license keys and usage for different time periods with the License Reporting Manager. A historical record of the utilization per license key is maintained in the vCenter Server database. See the vSphere Datacenter Administration Guide.
* Power Management Improvements. ESX 4.1 takes advantage of deep sleep states to further reduce power consumption during idle periods. The vSphere Client has a simple user interface that allows you to choose one of four host power management policies. In addition, you can view the history of host power consumption and power cap information on the vSphere Client Performance tab on newer platforms with integrated power meters. See the vSphere Datacenter Administration Guide.
Platform Enhancements
* Performance and Scalability Improvements. vSphere 4.1 includes numerous enhancements that increase performance and scalability.
o vCenter Server 4.1 can support three times more virtual machines and hosts per system, as well as more concurrent instances of the vSphere Client and a larger number of virtual machines per cluster than vCenter Server 4.0. The scalability limits of Linked Mode, vMotion, and vNetwork Distributed Switch have also increased.
o New optimizations have been implemented for AMD-V and Intel VT-x architectures, while memory utilization efficiency has been improved still further using Memory Compression. Storage enhancements have led to significant performance improvements in NFS environments. VDI operations, virtual machine provisioning and power operations, and vMotion have enhanced performance as well.
See Configuration Maximums for VMware vSphere 4.1.
* Reduced Overhead Memory. vSphere 4.1 reduces the amount of overhead memory required, especially when running large virtual machines on systems with CPUs that provide hardware MMU support (AMD RVI or Intel EPT).
* DRS Virtual Machine Host Affinity Rules. DRS provides the ability to set constraints that restrict placement of a virtual machine to a subset of hosts in a cluster. This feature is useful for enforcing host-based ISV licensing models, as well as keeping sets of virtual machines on different racks or blade systems for availability reasons. See the vSphere Resource Management Guide.
* Memory Compression. Compressed memory is a new level of the memory hierarchy, between RAM and disk. Slower than memory, but much faster than disk, compressed memory improves the performance of virtual machines when memory is under contention, because less virtual memory is swapped to disk. See the vSphere Resource Management Guide.
* vMotion Enhancements. In vSphere 4.1, vMotion enhancements significantly reduce the overall time for host evacuations, with support for more simultaneous virtual machine migrations and faster individual virtual machine migrations. The result is a performance improvement of up to 8x for an individual virtual machine migration, and support for four to eight simultaneous vMotion migrations per host, depending on the vMotion network adapter (1GbE or 10GbE respectively). See the vSphere Datacenter Administration Guide.
* ESX/ESXi Active Directory Integration. Integration with Microsoft Active Directory allows seamless user authentication for ESX/ESXi. You can maintain users and groups in Active Directory for centralized user management and you can assign privileges to users or groups on ESX/ESXi hosts. In vSphere 4.1, integration with Active Directory allows you to roll out permission rules to hosts by using Host Profiles. See the ESX Configuration Guide and the ESXi Configuration Guide.
* Configuring USB Device Passthrough from an ESX/ESXi Host to a Virtual Machine. You can configure a virtual machine to use USB devices that are connected to an ESX/ESXi host where the virtual machine is running. The connection is maintained even if you migrate the virtual machine using vMotion. See the vSphere Virtual Machine Administration Guide.
* Improvements in Enhanced vMotion Compatibility. vSphere 4.1 includes an AMD Opteron Gen. 3 (no 3DNow!™) EVC mode that prepares clusters for vMotion compatibility with future AMD processors. EVC also provides numerous usability improvements, including the display of EVC modes for virtual machines, more timely error detection, better error messages, and the reduced need to restart virtual machines. See the vSphere Datacenter Administration Guide.
Partner Ecosystem
* vCenter Update Manager Support for Provisioning, Patching, and Upgrading EMC's ESX PowerPath Module. vCenter Update Manager can provision, patch, and upgrade third-party modules that you can install on ESX, such as EMC's PowerPath multipathing software. Using the capability of Update Manager to set policies using the Baseline construct and the comprehensive Compliance Dashboard, you can simplify provisioning, patching, and upgrade of the PowerPath module at scale. See the vCenter Update Manager Installation and Administration Guide.
* User-configurable Number of Virtual CPUs per Virtual Socket. You can configure virtual machines to have multiple virtual CPUs reside in a single virtual socket, with each virtual CPU appearing to the guest operating system as a single core. Previously, virtual machines were restricted to having only one virtual CPU per virtual socket. See the vSphere Virtual Machine Administration Guide.
* Expanded List of Supported Processors. The list of supported processors has been expanded for ESX 4.1. To determine which processors are compatible with this release, use the Hardware Compatibility Guide. Among the supported processors is the Intel Xeon 7500 Series processor, code-named Nehalem-EX (up to 8 sockets).
_________________________________________________________________
2010年7月17日,重新上傳vCenter源;附加esx4.0-4.1、esxi4.0-4.1升級包。
_________________________________________________________________
2010年7月23日,增加Dell定制的ESXi4.1;原文件名:VMware-VMvisor-InstallerCD-4.1-260247.i386_DellCustomized_A00.iso

_________________________________________________________________
2010年8月02日,增加ESXi3.5-ESXi4.1升級包;原文件名:upgrade-from-ESXi3.5-to-4.1.0-0.0.260247-release.zip
_________________________________________________________________
2010年08月19日,增加"pre-upgrade-from-ESX4.0-to-4.1.0-0.0.260247-release.zip"
_________________________________________________________________
2010年09月11日,增加"VMware-vShield-Manager-4.1.0-287872.ova"
注:ova是一種預先設置好了的虛擬機“模板”,導入後就可以使用。
_________________________________________________________________
2011年03月06日,增加"VMware vShield 4.1u1"相關資源


_________________________________________________________________
2011年03月26日,增加“VMwareDataRecovery 1.2.1”相關資源
_________________________________________________________________
2011年04月14日,增加“VMware Workstation 2011”相關資源
_________________________________________________________________
2011年06月01日,增加"vSphere 4.0u3"部分資源
_________________________________________________________________
2011年06月29日,增加"vCenter Converter Standalone 5.0 Beta"資源
_________________________________________________________________
2011年08月26日,增加"vSphere 5.0"資源(逐步上傳,無VSA資源)
_________________________________________________________________
2011年09月03日,增加vSphere 5.0相關說明以及“vCenter Converter Standalone 5.0”正式版資源(beta版的資源即將刪除)
_________________________________________________________________
2011年11月06-08日,完善及增加"vSphere 4.0u3"和"vSphere 4.1u2"資源。
_________________________________________________________________
2011年12月22日,增加了"ESXi4.1"和"ESXi5.0"的補丁包資源。
_________________________________________________________________
- 上一頁:《游戲管理工具》(BinaryWorks eXtreme Games Manager)v1.0.3.3預破解版[壓縮包]
- 下一頁:《阿香婆視頻相冊制作軟件》(Ashampoo® Slideshow Studio HD 2)更新v2.0.4/多國語言版/含破解注冊表文件[壓縮包]
相關資源:
- [行業軟件]《Solid Works PhotoView 360 Overview SP0.0》2009[ISO]
- [多媒體類]《DVD完整復制工具軟件 白金版》(DVD-Cloner Platinum)更新v7.70.1000/含破解文件[壓縮包]
- [行業軟件]《Origin 8.0 SR4》(Origin 8.0 SR4)綠色英文版[壓縮包]
- [操作系統]《紅帽企業Linux服務器版 5 X86版本》(RedHat Enterprise Linux 5 Server X86)[ISO],操作系統、資源下載
- [編程開發]《風河VxWorks》(Tornado2.2 for ALL),編程開發、資源下載
- [行業軟件]《建築項目審閱解決方案》(Autodesk Navisworks Manage)V2012 WIN32/WIN64[光盤鏡像]
- [操作系統]《紅帽企業 Linux 5》(RedHat Enterprise Linux 5 Update 2)[ISO],操作系統、資源下載
- [應用軟件]《Nero6.6.0.12》(Nero6.6.0.12),應用軟件、資源下載
- [軟件綜合]photoshopcs6官方中文正式版+正版安裝序列號+安裝教程
- [行業軟件]《EPLAN Electric_P8_2.1.6電氣工程設計傳說中的CAE最佳軟件(又有人在taobao賣盜版)WIN7_32》(EPLAN Electric_P8_2.1.6)EPLAN Elect
- [其他圖書]《建築師叢書2012第二期》(Architect 2012-02)影印版
- [硬盤游戲]《龍珠mugen格斗怒氣爆發》(DragonBall Mugen Raging Blast)國慶正式版[壓縮包]
- [生活圖書]《醫經原旨》掃描版[PDF]
- [學習教程]《力行工作室:Flash CS4動畫制作與特效設計實例教程》[光盤鏡像]
- [行業軟件]《歐特克 ACADE 2012 簡體中文版》(Autodesk AutoCAD Electrical 2012)WIN32/WIN64.簡體中文版[安裝包]
- [經濟管理]《制造業目視管理標桿(掃描版)》(零隙精益生
- [多媒體類]《BBE效果插件包》(BBE.Sonic.Sweet.Bundle.VST.RTAS.v1.0)1.0[安裝包]
- [其他圖書]《柬埔寨 吳哥窟 紙模型》(柬埔寨 吳哥窟 紙模型
- [游戲綜合]《仙劍奇俠傳1》98柔情篇windows xp環境完美修正版(絕版)(pal)2008.8.1完美修正版
- [操作系統]《Mandriva Linux 》(Mandriva.Linux.Powerpack )2011.i586[光盤鏡像]
- 《福昕PDF電子文檔套件[綠色中文純淨版]》(Foxit Phantom)2.0.0.0330[壓縮包]
- 《Visio 2003 sp2 精簡版》build 2005.09.29,應用軟件、資源下載
- 《刺繡軟件》(Tajima DGML XI)[Bin]
- 《Mindgenius business 2005》15.0.0.591[安裝包]
- 《FLASH相冊制作軟件》(Alivemedia Flash Slideshow Maker)v1.2.0.8/含注冊碼[壓縮包]
- 《客戶關系管理》(Combit Relationship Manager v2007 BiLiNGUAL)[Bin]
- 《Sony 時間屏保》,應用軟件、資源下載
- 《文件管理工具》(GPSoftware Directory Opus x86 v9.1.1.7)[壓縮包],應用軟件、資源下載
- 《Solid EDGE V20英文版》V20[ISO]
- 《teltel撥號器》,應用軟件、資源下載
- 《條形碼設計和打印軟件》(Euro Plus NiceLabel Suite)v5.4.0.6913.Multilingual[壓縮包]
- 好貸計算器 1.0.0.506
免責聲明:本網站內容收集於互聯網,本站不承擔任何由於內容的合法性及健康性所引起的爭議和法律責任。如果侵犯了你的權益,請通知我們,我們會及時刪除相關內容,謝謝合作! 聯系信箱:[email protected]
Copyright © 電驢下載基地 All Rights Reserved



